Introduction
Designing for resilience and sustainability has become an essential principle in modern architecture and planning. As global challenges such as climate change and resource depletion intensify, the need for Sustainable design has never been more pressing. By embracing Sustainable design principles, we can create environments that are not only energy-efficient but also resilient to future uncertainties. This approach seeks to balance ecological integrity, social equity, and economic viability, ensuring that structures and systems stand the test of time. Through thoughtful integration of natural resources, innovative technologies, and adaptable strategies, it is possible to foster spaces that thrive in harmony with the environment. As we move towards more conscious ways of living and building, Sustainable design offers a pathway to long-term sustainability, both for individuals and communities. It’s time to rethink how we approach the spaces we occupy

Table of Contents
The Principles of Resilient and Sustainable Design
The principles of resilient and Sustainable design revolve around creating systems that endure both environmental and societal shifts. It focuses on minimizing resource consumption while maximizing adaptability. By integrating renewable materials, optimizing energy use, and fostering ecological balance, Sustainable design ensures long-term functionality. Resilience within this framework emphasizes the ability to withstand and recover from challenges, supporting a harmonious coexistence with nature.
Core Concepts of Resilience in Modern Design
Core concepts of resilience in modern design focus on creating structures that can withstand and adapt to environmental and societal changes. In Sustainable design, resilience means not only durability but also the capacity to evolve in response to shifting needs and climate conditions. This involves using adaptive materials, innovative technologies, and planning for future uncertainties. By prioritizing flexibility, energy efficiency, and resource conservation, Sustainable design aims to foster long-term viability while minimizing negative environmental impacts. Resilient designs ultimately enhance the functionality and sustainability of both urban and rural spaces.
Sustainability: Beyond Eco-Friendly Materials
Sustainability in Sustainable design extends far beyond the use of eco-friendly materials. It encompasses an integrated approach that considers the entire lifecycle of a product or system, from sourcing to disposal. True sustainability involves energy efficiency, water conservation, and waste reduction, ensuring minimal environmental impact throughout. Moreover, it emphasizes design strategies that promote longevity, adaptability, and resource conservation. By adopting a holistic mindset, Sustainable design aims to foster a balance between ecological responsibility and human well-being, creating spaces that are both functional and enduring.
Balancing Aesthetics, Functionality, and Longevity
Balancing aesthetics, functionality, and longevity is a cornerstone of Sustainable design. It involves crafting spaces that are visually appealing while serving practical needs and enduring over time. Achieving this balance requires thoughtful consideration of materials, design choices, and user needs. Aesthetics should enhance the experience without compromising durability or utility. Functionality ensures spaces remain adaptable and efficient, while longevity focuses on creating enduring solutions that minimize waste. In Sustainable design, this balance promotes resilience and ensures that both beauty and purpose coexist harmoniously for the long term
Practical Steps for Simplified Resilient Design
Practical steps for simplified resilient design focus on integrating Sustainable design principles at every stage. Start by selecting durable materials that require minimal maintenance. Incorporate energy-efficient technologies and consider adaptive design strategies that allow for future flexibility. These measures reduce environmental impact while ensuring that spaces remain functional and resilient over time.
Identifying Key Vulnerabilities in Your Environment
Identifying key vulnerabilities in your environment is a critical first step in achieving Sustainable design. Begin by assessing factors such as climate risks, resource availability, and energy consumption patterns. Understand how these vulnerabilities may affect the long-term viability of a space. Pay attention to areas prone to natural disasters, energy inefficiency, and excessive waste. By pinpointing weaknesses, it becomes easier to implement targeted solutions, such as resilient materials and energy-efficient systems. Sustainable design aims to address these vulnerabilities with strategies that promote long-term stability, reduce environmental impact, and ensure adaptability to future challenges.
Choosing Durable and Sustainable Materials
Choosing durable and sustainable materials is essential for any project rooted in Sustainable design. It involves selecting resources that are both long-lasting and environmentally responsible. Opt for materials that are renewable, non-toxic, and require minimal energy during production. Consider natural elements such as bamboo, reclaimed wood, and low-impact metals. Durability ensures that materials withstand wear and tear, reducing the need for replacements and minimizing waste. In Sustainable design, the choice of materials not only impacts the aesthetic and functional aspects of a space but also its overall environmental footprint, fostering a future-proof approach to construction and design.
Streamlining Systems for Efficiency and Adaptability
Streamlining systems for efficiency and adaptability is crucial in achieving Sustainable design. This process involves simplifying complex systems to reduce energy consumption, waste, and resource use. By integrating intelligent technologies, such as smart grids and energy-efficient appliances, spaces become more responsive to changing needs. Additionally, adaptive design solutions allow spaces to evolve with minimal disruption. In Sustainable design, creating flexible systems ensures that structures can adjust to future demands while minimizing their environmental impact. This approach not only fosters long-term sustainability but also improves the functionality and resilience of spaces, offering solutions that are both practical and forward-thinking.
Integrated Systems Approach for Sustainability
An integrated systems approach for sustainability in Sustainable design involves coordinating various elements—energy, water, materials, and waste—into a cohesive, efficient system. By considering the interconnections between these components, it’s possible to reduce resource consumption, enhance performance, and promote long-term resilience. This holistic strategy fosters harmony between environmental, social, and economic factors
The Role of Energy Efficiency in Sustainable Design
Energy efficiency plays a pivotal role in Sustainable design, reducing the environmental footprint of buildings and systems. By optimizing energy use, it minimizes waste and lowers long-term operational costs. Key strategies include using high-performance insulation, efficient HVAC systems, and renewable energy sources. In Sustainable design, energy efficiency is not only about cutting costs but also about fostering resilience and sustainability. It ensures that buildings function harmoniously with their environment, promoting long-term sustainability and reducing reliance on nonrenewable resources.
Harnessing Renewable Resources for Long-Term Resilience
Harnessing renewable resources is crucial for long-term resilience in Sustainable design. By utilizing solar, wind, and geothermal energy, buildings can operate independently of finite fossil fuels. These renewable sources not only reduce environmental impact but also ensure energy security over time. In Sustainable design, integrating renewable resources helps create self-sustaining environments that adapt to future challenges, fostering both ecological balance and energy autonomy. Such approaches enhance resilience by reducing dependency on external systems and mitigating climate-related risks.
Smart Technology: Merging Innovation with Sustainability
Smart technology is revolutionizing Sustainable design by seamlessly merging innovation with environmental responsibility. By incorporating smart systems such as energy-efficient lighting, automated heating, and real-time monitoring, buildings can optimize their resource consumption. These technologies enable adaptive responses to changing conditions, ensuring that energy use is both efficient and minimized. In Sustainable design, smart technology offers the potential for intelligent decision-making, allowing systems to learn and evolve. This approach not only enhances sustainability but also reduces long-term costs, fostering a more resilient future. With constant advancements, smart tech is becoming essential in creating eco-conscious, functional, and energy-efficient spaces
Overcoming Common Challenges in Sustainable Design
Overcoming common challenges in Sustainable design involves addressing high upfront costs, limited resources, and integrating innovative technologies. By prioritizing long-term savings and durability, these obstacles can be mitigated. Strategic planning, material selection, and adopting energy-efficient systems allow designers to navigate these hurdles, creating spaces that balance environmental responsibility with practical functionality.
Addressing Budget Constraints Without Sacrificing Quality
Addressing budget constraints in Sustainable design requires strategic choices that balance cost and quality. Opting for locally sourced materials can reduce transportation costs while supporting sustainability. Prioritizing energy-efficient systems and smart technologies ensures long-term savings. By carefully selecting durable, low-maintenance components, high-quality design can be achieved without sacrificing functionality. Efficient planning and phased implementation allow for cost-effective investments that uphold both environmental integrity and financial feasibility, making Sustainable design accessible and achievable within a budget.
Navigating Regulatory Requirements and Incentives
Navigating regulatory requirements and incentives is crucial for implementing Sustainable design effectively. Understanding local building codes, environmental standards, and government policies ensures compliance while optimizing project outcomes. Incentives such as tax credits, grants, and rebates for energy-efficient technologies can significantly reduce costs. By aligning design strategies with these regulations and taking advantage of available benefits, Sustainable design becomes more feasible and financially viable, promoting eco-conscious practices within legal frameworks. This approach not only enhances sustainability but also ensures long-term success and efficiency.
Educating Stakeholders on the Value of Resilient Design
Educating stakeholders on the value of resilient design is essential for promoting Sustainable design practices. Clear communication about the long-term benefits—such as reduced operational costs, improved energy efficiency, and enhanced environmental impact—helps gain support. Demonstrating how Sustainable design mitigates risks, adapts to climate change, and ensures durability builds a stronger case. By fostering understanding and engagement, stakeholders can make informed decisions that prioritize sustainability, leading to more responsible, forward-thinking design choices
Real-Life Applications of Resilient and Sustainable Design
Real-life applications of Sustainable design include energy-efficient buildings, green infrastructure, and adaptive reuse of materials. Urban developments utilize renewable resources, while residential projects focus on low-impact living with eco-friendly materials. These practical implementations demonstrate how Sustainable design not only conserves resources but also enhances the resilience of environments, ensuring long-term viability.
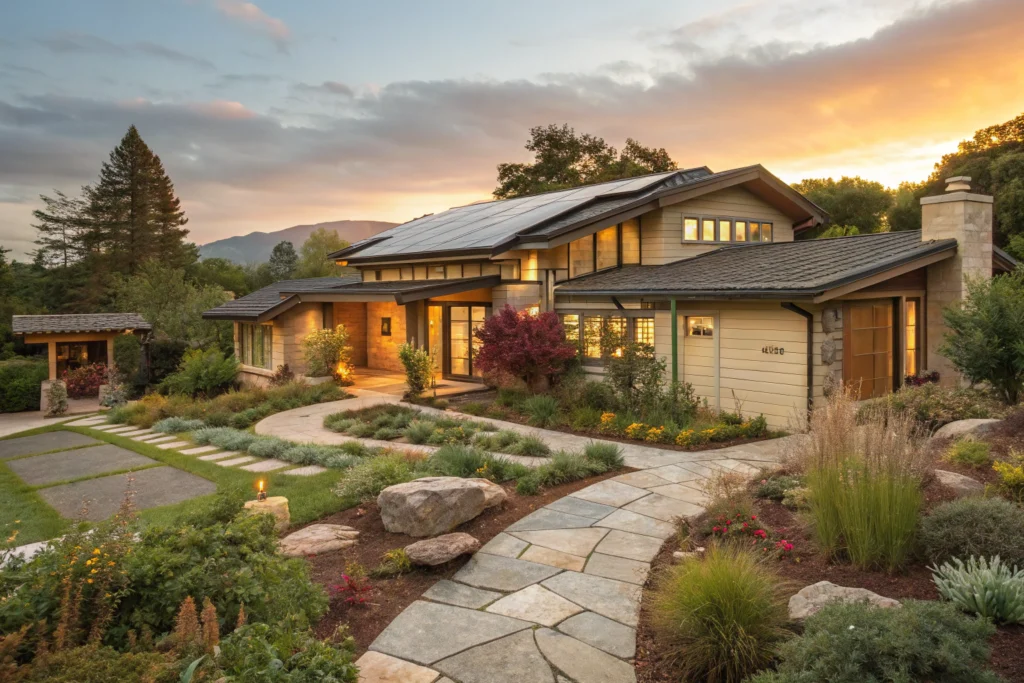

Case Studies: Homes Built for Longevity and Efficiency
Case studies of homes built for longevity and efficiency highlight the practical benefits of Sustainable design. For example, some homes incorporate passive solar design, maximizing natural light while minimizing energy consumption. Others integrate durable, low-maintenance materials like reclaimed wood and concrete, ensuring longevity. Rainwater harvesting systems, energy-efficient appliances, and solar panels are common features that contribute to reduced carbon footprints. These homes demonstrate how Sustainable design practices can create comfortable, energy-efficient living spaces that stand the test of time, all while contributing positively to the environment and reducing long-term costs.
Urban Planning: Creating Resilient Cities for the Future
Urban planning plays a crucial role in creating resilient cities that can withstand the challenges of the future. By prioritizing Sustainable design, cities can integrate green spaces, renewable energy solutions, and efficient public transportation systems. Incorporating adaptive infrastructure helps manage climate risks, such as flooding and extreme heat. Compact, mixed-use neighborhoods encourage walkability and reduce reliance on cars, fostering a healthier, more sustainable urban lifestyle. The future of urban planning lies in creating cities that not only meet the needs of today but are prepared for the uncertainties of tomorrow, ensuring a harmonious balance between growth and environmental preservation.
Designing Workspaces That Adapt and Endure
Designing workspaces that adapt and endure requires a focus on both flexibility and resilience. By incorporating Sustainable design principles, these environments can evolve with changing needs while minimizing their environmental impact. Modular furniture and versatile layouts allow spaces to be reconfigured as required, ensuring long-term utility. Incorporating natural lighting, energy-efficient materials, and green elements further enhances the space’s sustainability. Furthermore, creating workspaces that foster collaboration and well-being boosts productivity and employee satisfaction. These thoughtful designs not only support the modern workforce but also ensure that workspaces remain functional and resilient for years to come.

Conclusion
In conclusion, embracing Sustainable design is essential for creating resilient and adaptive spaces that thrive in the face of evolving environmental and societal challenges. By prioritizing durability, energy efficiency, and environmental responsibility, designers can create lasting solutions that benefit both people and the planet. Whether applied to homes, workspaces, or urban environments, Sustainable design encourages a holistic approach that integrates innovative materials, energy-efficient technologies, and adaptable systems. This comprehensive mindset not only mitigates risks associated with climate change but also ensures that spaces remain functional and efficient for future generations. As we continue to advance, the commitment to sustainable practices will play a pivotal role in shaping a more sustainable, resilient world.

